Reseeding monocultures to increase grass production
Description
Description of the innovation
The 10 Steps to Reseeding
- Identify under-performing paddocks for reseeding
- Plan to reseed early
- Soil test –Before reseeding
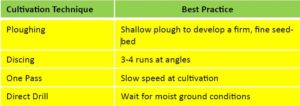
- Spray off paddock
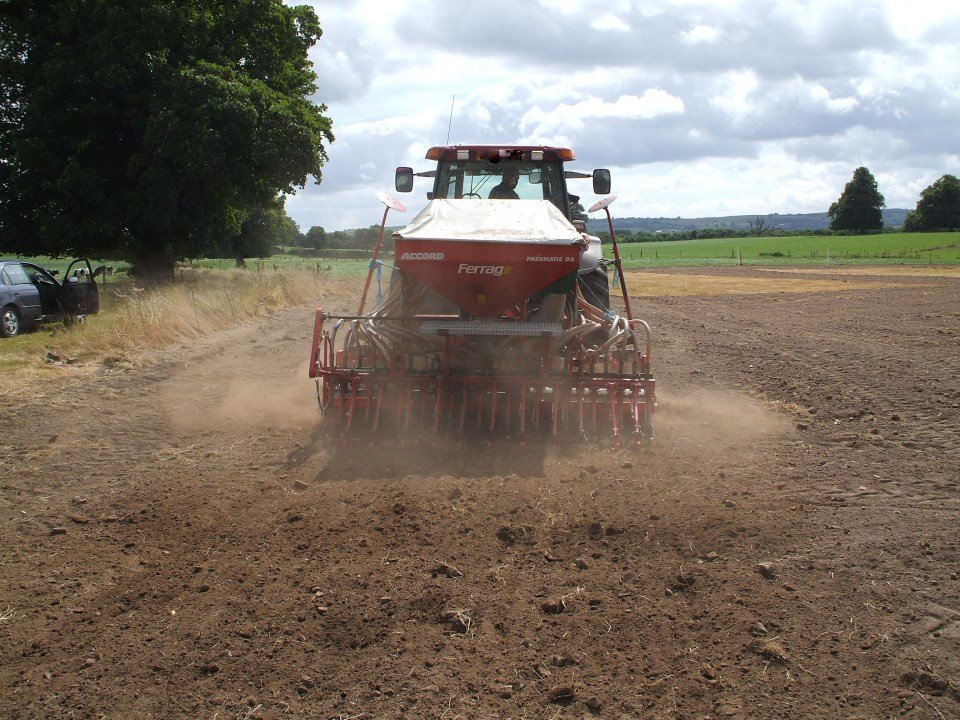
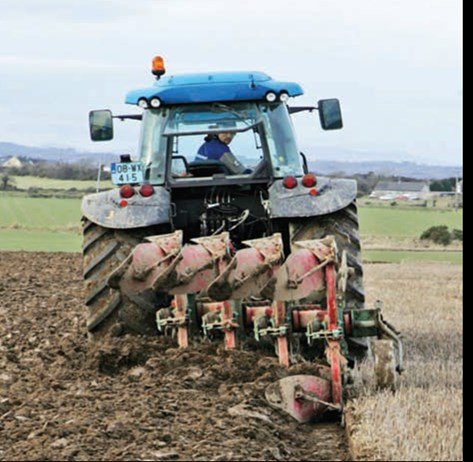
- Prepare a firm, fine seed bed
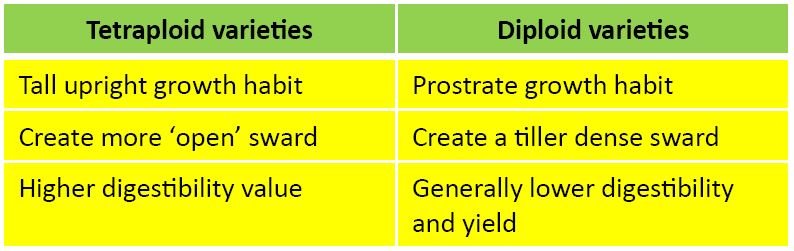
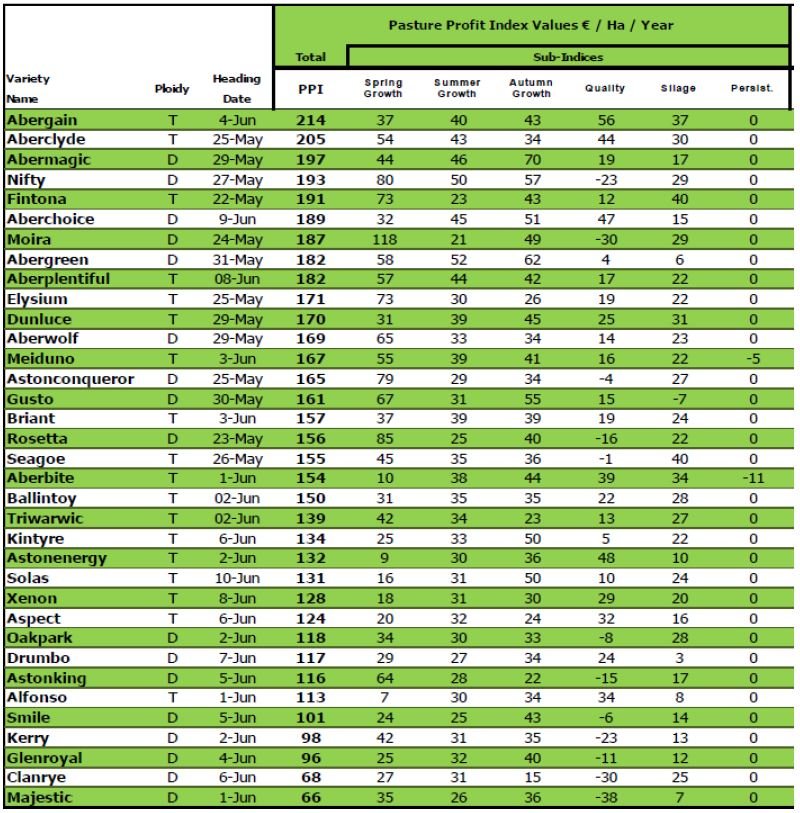
- Choose the most profitable varieties (Use Pasture Profit Index)
- Spread lime and N,P and K
- Roll after sowing
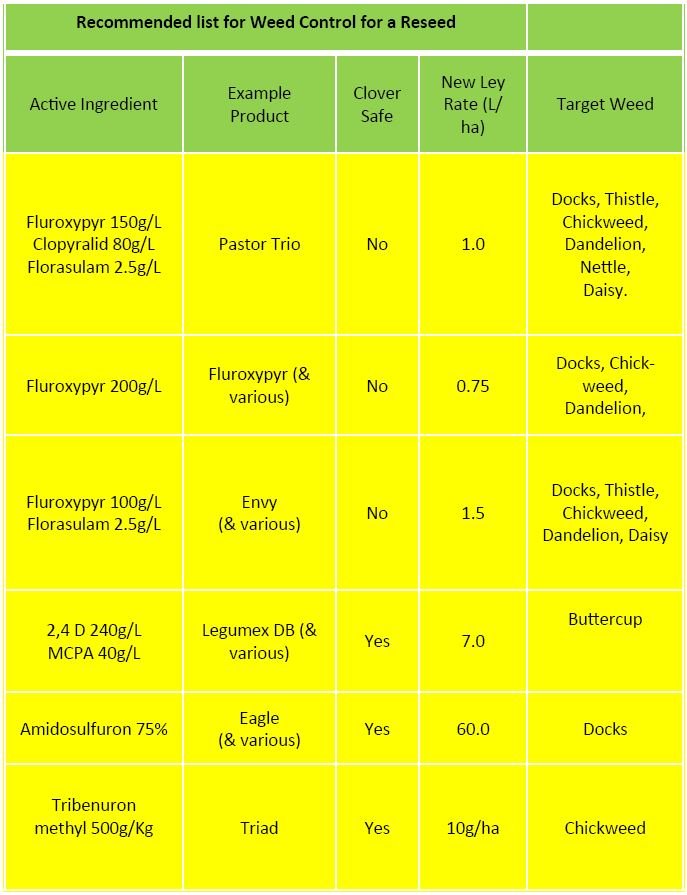
- Post emergence spra
- Graze at a low cover (700kg-1000kgDM/ha)
Advantages
- Increase the overall productivity of the farm (sales, farm output & silage production)
- Allow higher animal output per hectare relative to permanent pasture
- Increase grass quality and utilisa-tion (profit!)
Disadvantages
- Soil fertility needs to be correct on the farm before reseeding
- Farmer must do everything cor-rect to ensure good germination rates
- Resseding can be expensive when not carried out correctly
Cultivation
- All methods effective when carried out correctly
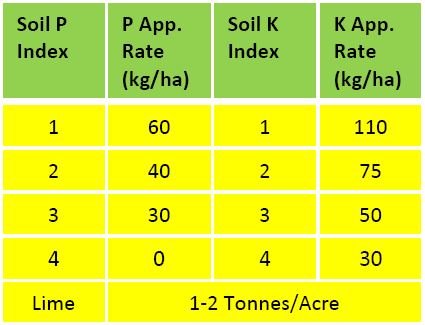
Soil Fertility
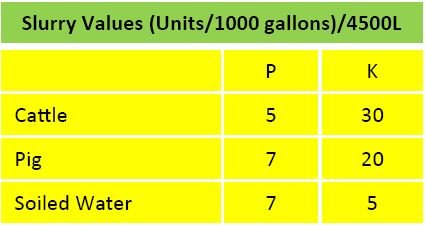
- Soil test, lime and appropriate fertiliser (N, P & K) (2.5 T lime/acre) (3 bags 10-10-20/acre)
- Lime- Increase seed germination
- Optimum pH – 6.3, P: Index 3 and K: index 4
- Post sowing management
- Ensure seed bed is rolled following seeding
- +30 Units N/Acre (Weeks 4-5)
- Post emergence spray – 5-6 weeks after re-seeding (best time to control docks)
- 1st grazing – 700 – 1000 kg DM/ha
- Graze every 17 – 21 days (1000 – 1400 kg DM/ha)
- Check for uniform establishment (pests)
- Avoid silage in first year if possible
More information
Additional information
| Domains of innovation | forage mixture |
|---|---|
| Main types of animal | beef cattle, dairy cattle, meat sheep |
| Country | Ireland |
| Product type | Technical leaflet |
| Language | English |